Getting started with LXD opens the door to efficient and lightweight container and virtual machine management on Linux. LXD is a powerful system container and VM manager that simplifies the deployment and management of Linux containers, making it an ideal solution for hosting web applications, testing environments, and deploying microservices. It bridges the gap between traditional virtualization and containerization, offering flexibility and performance for modern infrastructure needs.
In this article, we’ll guide you through a step-by-step demo to install and manage a container using LXD for a practical scenario. Additionally, we’ll provide a summarized cheat sheet in table format to help you quickly reference essential LXD commands, ensuring you have the tools you need to streamline your container management workflows.
Previous articles:
01. Introduction to Ubuntu Server – SysOSX: AI & Cloud
02. How to Setup Your First Ubuntu Server: A Beginner’s Guide – SysOSX: AI & Cloud
03.Mastering the Linux Command Line for Ubuntu Server – SysOSX: AI & Cloud
04. Managing Users and Permissions on Ubuntu Server: A Comprehensive Guide – SysOSX: AI & Cloud
05. Networking Basics for Ubuntu Server: A Comprehensive Guide – SysOSX: AI & Cloud
06. Installing and Managing Software on Ubuntu Server: A Complete Guide – SysOSX: AI & Cloud
07.Patching and Updating Ubuntu Server: A Comprehensive Guide – SysOSX: AI & Cloud
08. Securing Your Ubuntu Server: Practical Steps for Hardening and Protection – SysOSX: AI & Cloud
09. Ubuntu server auditing and logging
10. System Monitoring Tools for Ubuntu Server: A Comprehensive Guide – SysOSX: AI & Cloud
11. Centralized Logging for ubuntu server: a must read guide – SysOSX: AI & Cloud
12. Audit and Compliance for Ubuntu Server: Best Practices – SysOSX: AI & Cloud
14. Host Multiple Websites on a single Ubuntu Server: Useful tips – SysOSX: AI & Cloud
15. Managing Storage and Disks on Ubuntu Server: Simple Guide – SysOSX: AI & Cloud
16. Setting Up File Sharing Services on Ubuntu Server: a complete guide – SysOSX: AI & Cloud
17. Setting Up a Secure Database Server on Ubuntu: MySQL vs. MariaDB – SysOSX: AI & Cloud
18. How to Configure and Use LVM on Ubuntu Server: A Comprehensive Guide – SysOSX: AI & Cloud
Table of Contents
What is LXD?
LXD is an open-source container management tool built on top of Linux Containers (LXC). It offers system containers that behave like virtual machines but are faster and more lightweight. With LXD, you can:
- Run full Linux distributions inside containers.
- Use advanced networking and storage features.
- Manage containers remotely via REST API.
- Migrate containers between hosts with minimal downtime.
Installing LXD Using Snap
The recommended way to install LXD on modern Ubuntu systems is via Snap. Follow these steps:
1. Install Snapd
Ensure Snap is installed on your system. If Snap is not installed, run:
sudo apt update
sudo apt install snapd
2. Install LXD
Install LXD using Snap:
sudo snap install lxd

3. Verify Installation
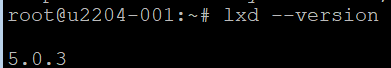
Check the installed version of LXD:
lxd --version
Demo: Using LXD to Install a Container
Let’s walk through a common scenario where we use LXD to create and manage a container running Ubuntu 22.04.
Step 1: Initialize LXD
Run the following command to initialize LXD:
sudo lxd init
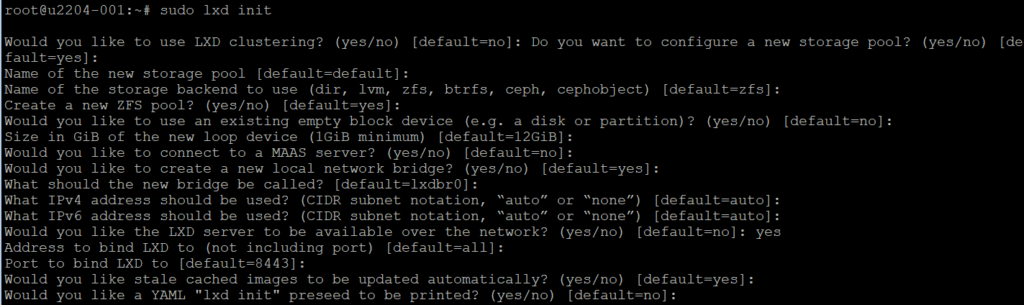
You will be prompted to configure storage, networking, and other settings. For simplicity, you can choose the default options.
Step 2: Launch an Ubuntu Container
Create and start a container running Ubuntu 22.04 with the command:
lxc launch ubuntu:22.04 web-server
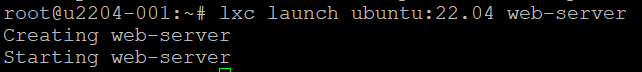
This command creates a container named web-server using the Ubuntu 22.04 image.
Step 3: Access the Container
Get shell access to the container:
lxc exec web-server -- bash

You are now inside the container and can install packages or configure services. For example, install Apache:
apt update
apt install apache2 -y
Start the Apache service:
systemctl start apache2
Step 4: Verify Container Networking
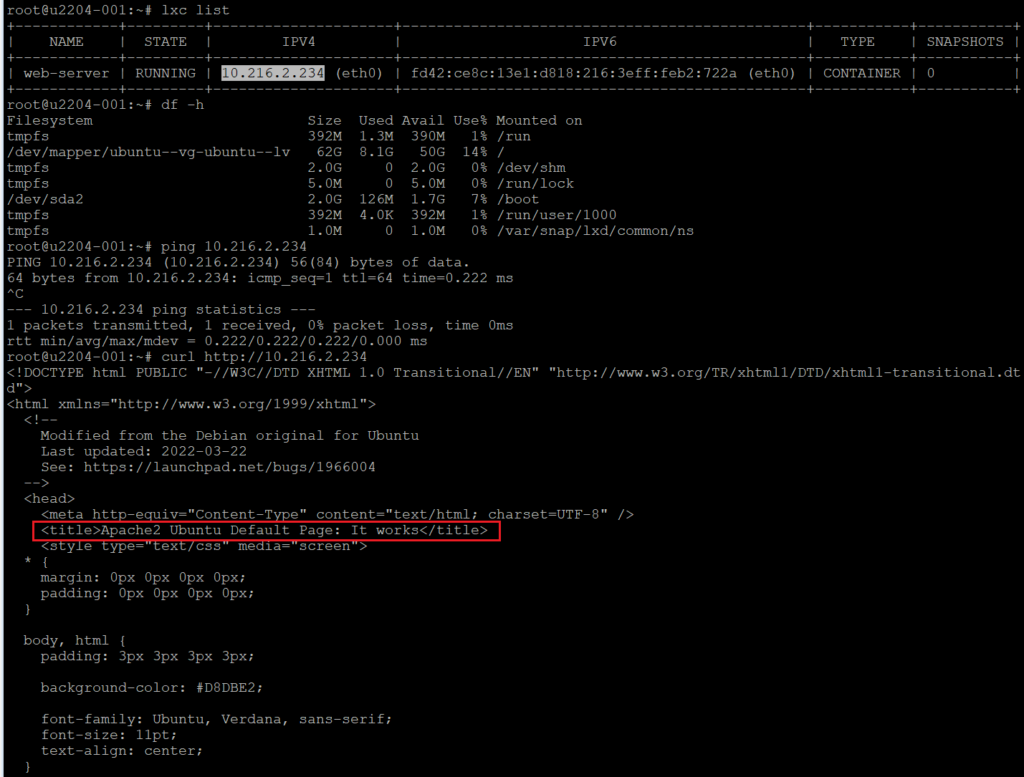
Exit the container and check its IP address:
lxc list

Access the container’s web server by visiting its IP address in a browser or using curl http://ip to check the connectivity.
Step 5: Stop and Delete the Container
When you no longer need the container, stop it:
lxc stop web-server
Delete the container:
lxc delete web-server
LXD Command line Cheat Sheet
Below is a summarized cheat sheet for commonly used LXD commands:
| Category | Command | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Initialization | lxd init | Initializes LXD before first use. |
| Create Instances | lxc init <image> <name> | Creates a container without starting it. |
lxc launch <image> <name> | Creates and starts a container. | |
lxc launch <image> <name> --vm | Creates and starts a virtual machine. | |
| Manage Instances | lxc list | Lists all instances. |
lxc info <instance> | Displays information about an instance. | |
lxc start <instance> | Starts an instance. | |
lxc stop <instance> [--force] | Stops an instance. | |
| `lxc delete <instance> [–force | –interactive]` | |
| Access Instances | lxc exec <instance> -- <command> | Runs a command inside an instance. |
lxc exec <instance> -- bash | Gets shell access to an instance. | |
lxc console <instance> | Gets console access to an instance. | |
| File Management | lxc file pull <instance>/<path> <local_path> | Pulls a file from an instance. |
lxc file push <local_path> <instance>/<path> | Pushes a file to an instance. | |
| Projects | lxc project create <project> | Creates a project. |
lxc project set <project> <option> | Configures a project. | |
lxc project switch <project> | Switches to a project. |
Official Document:
First steps with LXD
Conclusion
LXD simplifies container management, making it an excellent choice for developers, system administrators, and DevOps engineers. With its lightweight performance and VM-like capabilities, LXD is ideal for hosting applications, testing environments, and more.
In this article, we demonstrated how to use LXD to install and manage a container for a common scenario. Additionally, the cheat sheet provides a quick reference for essential LXD commands.
Next Topic:
In next article we will talk about how to use podman on ubuntu server. Stay tuned.